Pstn Telephony Software
Voice over IP Wikipedia. Voice over Internet Protocol also voice over IP, Vo. IP or IP telephony is a methodology and group of technologies for the delivery of voice communications and multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol IP networks, such as the Internet. Pstn Telephony Software' title='Pstn Telephony Software' />
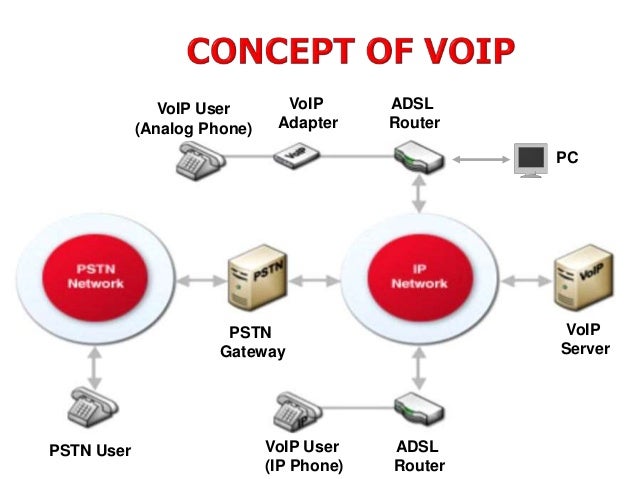 The terms Internet telephony, broadband telephony, and broadband phone service specifically refer to the provisioning of communications services voice, fax, SMS, voice messaging over the public Internet, rather than via the public switched telephone network PSTN. The steps and principles involved in originating Vo. Voice Solutions. Silicon Labs highly integrated voice ICs are the smallest, most costeffective solutions available for a wide range of telephony, voice over. Voice tutorial explaining traditional analog voice technology, Voice over IP, IP Telephony, G. G. 729, G. 723, PCM, Mea Opinion Score, Class of Service and ADPCM. Pstn Telephony Software' title='Pstn Telephony Software' />IP telephone calls are similar to traditional digital telephony and involve signaling, channel setup, digitization of the analog voice signals, and encoding. Instead of being transmitted over a circuit switched network, the digital information is packetized, and transmission occurs as IP packets over a packet switched network. They transport media streams using special media delivery protocols that encode audio and video with audio codecs, and video codecs. Various codecs exist that optimize the media stream based on application requirements and network bandwidth some implementations rely on narrowband and compressed speech, while others support high fidelity stereo codecs. Some popular codecs include law and a law versions of G. G. 7. 22, an open source voice codec known as i. LBC, a codec that only uses 8 kbits each way called G. Early providers of voice over IP services offered business models and technical solutions that mirrored the architecture of the legacy telephone network. Second generation providers, such as Skype, built closed networks for private user bases, offering the benefit of free calls and convenience while potentially charging for access to other communication networks, such as the PSTN. This limited the freedom of users to mix and match third party hardware and software. Third generation providers, such as Google Talk, adopted the concept of federated Vo. IPwhich is a departure from the architecture of the legacy networks. These solutions typically allow dynamic interconnection between users on any two domains on the Internet when a user wishes to place a call. In addition to Vo. IP phones, Vo. IP is available on many personal computers and other Internet access devices. Calls and SMS text messages may be sent over mobile data or Wi Fi. PronunciationeditVo. IP is variously pronounced as an initialism, V O I P, or as an acronym, usually vjp voyp, as in voice,3 but pronunciation in full words, voice over Internet Protocol, or voice over IP, is sometimes used. ProtocolseditVoice over IP has been implemented in various ways using both proprietary protocols and protocols based on open standards. These protocols can be used by a Vo. IP phone, special purpose software, a mobile application or integrated into a web page. Vo. IP protocols include Session Initiation Protocol SIP, connection management protocol developed by the IETFH. Vo. IP call signaling and control protocols that found widespread implementation. Since the development of newer, less complex protocols such as MGCP and SIP, H. Media Gateway Control Protocol MGCP, connection management for media gateways. H. 2. 48, control protocol for media gateways across a converged internetwork consisting of the traditional public switched telephone network PSTN and modern packet networks. Real time Transport Protocol RTP, transport protocol for real time audio and video data. Real time Transport Control Protocol RTCP, sister protocol for RTP providing stream statistics and status information. Secure Real time Transport Protocol SRTP, encrypted version of RTPSession Description Protocol SDP, file format used principally by SIP to describe Vo. IP connections. Inter Asterisk e. Xchange IAX, protocol used between Vo. IP servers. XMPP, instant messaging, presence information, and contact list maintenance. Jingle, adds peer to peer session control to XMPPSkype protocol, proprietary Internet telephony protocol suite based on peer to peer architecture. AdoptioneditConsumer marketedit. Example of residential network including Vo. IPMass market Vo. IP services use existing broadband Internet access, by which subscribers place and receive telephone calls in much the same manner as they would via the public switched telephone network PSTN. Full service Vo. IP phone companies provide inbound and outbound service with direct inbound dialing. Many offer unlimited domestic calling and sometimes international calls for a flat monthly subscription fee. Phone calls between subscribers of the same provider are usually free when flat fee service is not available. A Vo. IP phone is necessary to connect to a Vo. IP service provider. This can be implemented in several ways Dedicated Vo. IP phones connect directly to the IP network using technologies such as wired Ethernet or Wi Fi. These are typically designed in the style of traditional digital business telephones. An analog telephone adapter connects to the network and implements the electronics and firmware to operate a conventional analog telephone attached through a modular phone jack. Some residential Internet gateways and cablemodems have this function built in. Softphone application software installed on a networked computer that is equipped with a microphone and speaker, or headset. The application typically presents a dial pad and display field to the user to operate the application by mouse clicks or keyboard input. PSTN and mobile network providerseditIt is becoming increasingly common for telecommunications providers to use Vo. IP telephony over dedicated and public IP networks to connect switching centers and to interconnect with other telephony network providers this is often referred to as IP backhaul. Smartphones and Wi Fi enabled mobile phones may have SIP clients built into the firmware or available as an application download. Corporate useeditBecause of the bandwidth efficiency and low costs that Vo. IP technology can provide, businesses are migrating from traditional copper wire telephone systems to Vo. IP systems to reduce their monthly phone costs. Fifa 08 Demo Next-Gen Patch. In 2. 00. 8, 8. 0 of all new Private branch exchange PBX lines installed internationally were Vo. IP. 6Vo. IP solutions aimed at businesses have evolved into unified communications services that treat all communicationsphone calls, faxes, voice mail, e mail, Web conferences, and moreas discrete units that can all be delivered via any means and to any handset, including cellphones. Ea Sports Active More Workouts Isometric Exercises. Two kinds of competitors are competing in this space one set is focused on Vo. IP for medium to large enterprises, while another is targeting the small to medium business SMB market. Vo. IP allows both voice and data communications to be run over a single network, which can significantly reduce infrastructure costs. The prices of extensions on Vo. IP are lower than for PBX and key systems. Vo. IP switches may run on commodity hardware, such as personal computers. Rather than closed architectures, these devices rely on standard interfaces. Vo. IP devices have simple, intuitive user interfaces, so users can often make simple system configuration changes. Dual mode phones enable users to continue their conversations as they move between an outside cellular service and an internal Wi Fi network, so that it is no longer necessary to carry both a desktop phone and a cell phone.
The terms Internet telephony, broadband telephony, and broadband phone service specifically refer to the provisioning of communications services voice, fax, SMS, voice messaging over the public Internet, rather than via the public switched telephone network PSTN. The steps and principles involved in originating Vo. Voice Solutions. Silicon Labs highly integrated voice ICs are the smallest, most costeffective solutions available for a wide range of telephony, voice over. Voice tutorial explaining traditional analog voice technology, Voice over IP, IP Telephony, G. G. 729, G. 723, PCM, Mea Opinion Score, Class of Service and ADPCM. Pstn Telephony Software' title='Pstn Telephony Software' />IP telephone calls are similar to traditional digital telephony and involve signaling, channel setup, digitization of the analog voice signals, and encoding. Instead of being transmitted over a circuit switched network, the digital information is packetized, and transmission occurs as IP packets over a packet switched network. They transport media streams using special media delivery protocols that encode audio and video with audio codecs, and video codecs. Various codecs exist that optimize the media stream based on application requirements and network bandwidth some implementations rely on narrowband and compressed speech, while others support high fidelity stereo codecs. Some popular codecs include law and a law versions of G. G. 7. 22, an open source voice codec known as i. LBC, a codec that only uses 8 kbits each way called G. Early providers of voice over IP services offered business models and technical solutions that mirrored the architecture of the legacy telephone network. Second generation providers, such as Skype, built closed networks for private user bases, offering the benefit of free calls and convenience while potentially charging for access to other communication networks, such as the PSTN. This limited the freedom of users to mix and match third party hardware and software. Third generation providers, such as Google Talk, adopted the concept of federated Vo. IPwhich is a departure from the architecture of the legacy networks. These solutions typically allow dynamic interconnection between users on any two domains on the Internet when a user wishes to place a call. In addition to Vo. IP phones, Vo. IP is available on many personal computers and other Internet access devices. Calls and SMS text messages may be sent over mobile data or Wi Fi. PronunciationeditVo. IP is variously pronounced as an initialism, V O I P, or as an acronym, usually vjp voyp, as in voice,3 but pronunciation in full words, voice over Internet Protocol, or voice over IP, is sometimes used. ProtocolseditVoice over IP has been implemented in various ways using both proprietary protocols and protocols based on open standards. These protocols can be used by a Vo. IP phone, special purpose software, a mobile application or integrated into a web page. Vo. IP protocols include Session Initiation Protocol SIP, connection management protocol developed by the IETFH. Vo. IP call signaling and control protocols that found widespread implementation. Since the development of newer, less complex protocols such as MGCP and SIP, H. Media Gateway Control Protocol MGCP, connection management for media gateways. H. 2. 48, control protocol for media gateways across a converged internetwork consisting of the traditional public switched telephone network PSTN and modern packet networks. Real time Transport Protocol RTP, transport protocol for real time audio and video data. Real time Transport Control Protocol RTCP, sister protocol for RTP providing stream statistics and status information. Secure Real time Transport Protocol SRTP, encrypted version of RTPSession Description Protocol SDP, file format used principally by SIP to describe Vo. IP connections. Inter Asterisk e. Xchange IAX, protocol used between Vo. IP servers. XMPP, instant messaging, presence information, and contact list maintenance. Jingle, adds peer to peer session control to XMPPSkype protocol, proprietary Internet telephony protocol suite based on peer to peer architecture. AdoptioneditConsumer marketedit. Example of residential network including Vo. IPMass market Vo. IP services use existing broadband Internet access, by which subscribers place and receive telephone calls in much the same manner as they would via the public switched telephone network PSTN. Full service Vo. IP phone companies provide inbound and outbound service with direct inbound dialing. Many offer unlimited domestic calling and sometimes international calls for a flat monthly subscription fee. Phone calls between subscribers of the same provider are usually free when flat fee service is not available. A Vo. IP phone is necessary to connect to a Vo. IP service provider. This can be implemented in several ways Dedicated Vo. IP phones connect directly to the IP network using technologies such as wired Ethernet or Wi Fi. These are typically designed in the style of traditional digital business telephones. An analog telephone adapter connects to the network and implements the electronics and firmware to operate a conventional analog telephone attached through a modular phone jack. Some residential Internet gateways and cablemodems have this function built in. Softphone application software installed on a networked computer that is equipped with a microphone and speaker, or headset. The application typically presents a dial pad and display field to the user to operate the application by mouse clicks or keyboard input. PSTN and mobile network providerseditIt is becoming increasingly common for telecommunications providers to use Vo. IP telephony over dedicated and public IP networks to connect switching centers and to interconnect with other telephony network providers this is often referred to as IP backhaul. Smartphones and Wi Fi enabled mobile phones may have SIP clients built into the firmware or available as an application download. Corporate useeditBecause of the bandwidth efficiency and low costs that Vo. IP technology can provide, businesses are migrating from traditional copper wire telephone systems to Vo. IP systems to reduce their monthly phone costs. Fifa 08 Demo Next-Gen Patch. In 2. 00. 8, 8. 0 of all new Private branch exchange PBX lines installed internationally were Vo. IP. 6Vo. IP solutions aimed at businesses have evolved into unified communications services that treat all communicationsphone calls, faxes, voice mail, e mail, Web conferences, and moreas discrete units that can all be delivered via any means and to any handset, including cellphones. Ea Sports Active More Workouts Isometric Exercises. Two kinds of competitors are competing in this space one set is focused on Vo. IP for medium to large enterprises, while another is targeting the small to medium business SMB market. Vo. IP allows both voice and data communications to be run over a single network, which can significantly reduce infrastructure costs. The prices of extensions on Vo. IP are lower than for PBX and key systems. Vo. IP switches may run on commodity hardware, such as personal computers. Rather than closed architectures, these devices rely on standard interfaces. Vo. IP devices have simple, intuitive user interfaces, so users can often make simple system configuration changes. Dual mode phones enable users to continue their conversations as they move between an outside cellular service and an internal Wi Fi network, so that it is no longer necessary to carry both a desktop phone and a cell phone.